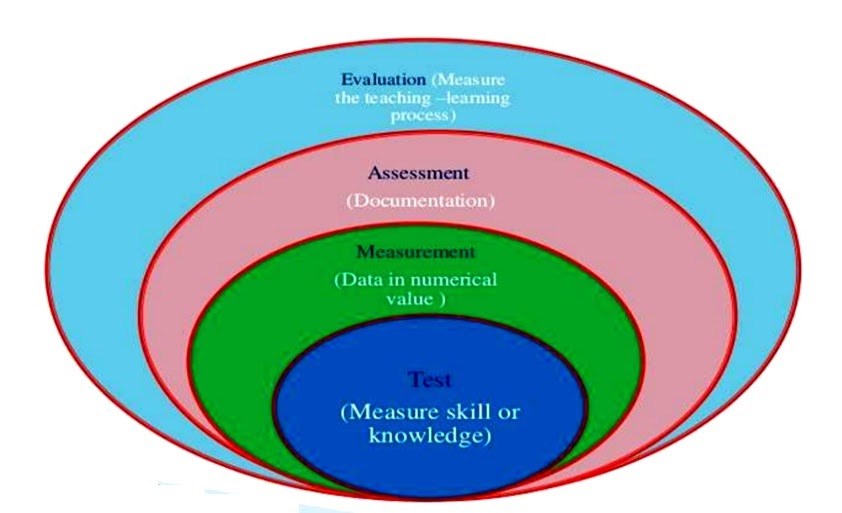
Test measurement and evaluation are crucial components in the fields of education, psychology, and various industries, helping to ensure that assessments are effective and reliable. In today’s fast-paced world, the ability to measure and evaluate performance accurately has become more important than ever. This guide will delve into the intricacies of test measurement and evaluation, providing insights that are essential for educators, professionals, and anyone interested in understanding this vital area.
The growing emphasis on data-driven decision-making in education and industry necessitates a thorough understanding of how tests are created, measured, and evaluated. This article will explore the principles of test measurement, various evaluation techniques, and the implications of these assessments in real-world settings. By the end of this article, readers will be equipped with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of test measurement and evaluation effectively.
Whether you are an educator seeking to optimize your assessment strategies or a professional aiming to enhance your evaluation techniques, understanding test measurement and evaluation will empower you to make informed decisions. Let’s embark on this journey to explore the essential aspects of this topic.
Table of Contents
- What is Test Measurement?
- Importance of Test Measurement
- Types of Tests
- Evaluation Techniques
- Reliability and Validity in Testing
- Test Administration
- Data Analysis in Test Measurement
- The Future of Test Measurement and Evaluation
What is Test Measurement?
Test measurement refers to the process of quantifying an individual's performance or ability using standardized assessments. It involves the development and administration of tests designed to measure specific skills, knowledge, or competencies. This process is vital in various fields, including education, psychology, and human resources.
Key Components of Test Measurement
- **Test Development:** The creation of assessment tools that accurately measure the desired attributes.
- **Standardization:** Ensuring that tests are administered and scored consistently across different populations.
- **Scoring Methods:** The techniques used to evaluate test results and provide meaningful interpretations.
Importance of Test Measurement
The significance of test measurement cannot be overstated. It serves several key purposes in various domains:
- Driving Instructional Decisions: Test results help educators tailor their teaching strategies to meet the needs of their students.
- Identifying Learning Gaps: Assessment data can reveal areas where students may be struggling, allowing for targeted interventions.
- Evaluating Program Effectiveness: Organizations can assess the impact of their programs and initiatives through systematic testing.
Types of Tests
There are several types of tests utilized in measurement and evaluation, each serving distinct purposes:
1. Formative Tests
Formative tests are conducted during the learning process to monitor student progress and provide feedback. They help instructors adjust their teaching methods based on student performance.
2. Summative Tests
Summative tests are administered at the end of an instructional period to evaluate student learning outcomes. These assessments provide a comprehensive overview of what students have achieved.
3. Diagnostic Tests
Diagnostic tests are designed to identify specific learning difficulties and areas of strength before instruction begins. They inform educators about the necessary support for each student.
4. Norm-Referenced Tests
These tests compare an individual's performance to a group’s average performance. They help in ranking students and understanding relative performance.
Evaluation Techniques
Effective evaluation techniques are essential for interpreting test results accurately. Here are some commonly used methods:
1. Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics summarize and describe the main features of data. They include measures such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation.
2. Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics allow researchers to make generalizations about a population based on sample data. Techniques include hypothesis testing and regression analysis.
3. Qualitative Assessments
Qualitative assessments provide insights into student learning through non-numeric data, such as observations and interviews, which can complement quantitative results.
Reliability and Validity in Testing
Reliability and validity are critical concepts in test measurement, determining the quality and effectiveness of the assessments.
1. Reliability
Reliability refers to the consistency of test scores over time. A reliable test will yield similar results under consistent conditions.
2. Validity
Validity assesses whether a test measures what it is intended to measure. Validity is essential for ensuring that the conclusions drawn from test results are accurate and meaningful.
Test Administration
Proper administration of tests is crucial to obtaining accurate and reliable results. Factors to consider include:
- Environment: The testing environment should be quiet and free from distractions.
- Instructions: Clear and concise instructions should be provided to all test-takers.
- Timing: Adequate time must be allotted for test completion to avoid undue pressure on participants.
Data Analysis in Test Measurement
Once tests are administered, analyzing the data is essential for making informed decisions. Data analysis involves:
- Data Cleaning: Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of the data collected.
- Statistical Analysis: Applying statistical techniques to interpret results and draw conclusions.
- Reporting Findings: Presenting results in a clear and actionable format for stakeholders.
The Future of Test Measurement and Evaluation
The landscape of test measurement and evaluation is evolving rapidly, influenced by technological advancements and new educational paradigms. Emerging trends include:
- Adaptive Testing: Tailoring assessments to individual test-taker abilities, providing a more personalized evaluation experience.
- Use of Artificial Intelligence: Leveraging AI to enhance test creation, administration, and analysis processes.
- Focus on Holistic Assessment: Recognizing the importance of non-cognitive skills and competencies in addition to traditional academic performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding test measurement and evaluation is essential for educators, professionals, and anyone involved in the assessment process. By grasping the key concepts of test types, evaluation techniques, reliability, and validity, you can enhance the quality of assessments and ensure that they serve their intended purpose effectively. We encourage you to apply this knowledge in your practice and share your experiences with us.
If you found this article informative, please leave a comment below, share it with your colleagues, or explore more articles on our site to deepen your understanding of test measurement and evaluation.
Penutup
Thank you for taking the time to read our comprehensive guide on test measurement and evaluation. We hope you found the information valuable and applicable to your needs. We invite you to return to our site for more insightful articles and resources that can support your learning journey.